- 1 in 7 households paid more than half of their income on housing in 2020.
- The US housing market is short 6.5 million homes
- Builders are facing bank funding shortages delaying new construction.
The United States is currently facing a severe housing shortage, which has led to elevated home prices and a highly competitive real estate market. This shortage is attributed to various factors, including rising materials costs, supply chain issues, labor shortages, and outdated zoning rules. The insufficient housing inventory has had significant impacts on both buyers and sellers, making homeownership unaffordable for many Americans and leading to skyrocketing rents and home prices. In this article, we will delve into the causes and consequences of the housing shortage and explore potential solutions to address this pressing issue.
The Housing Shortage Crisis
Insufficient Housing Inventory
The housing shortage crisis is characterized by a significant gap between the demand for housing and the available supply. According to a study conducted in 2022 by Up for Growth, a nonprofit research group, America has fallen 3.8 million homes short of meeting housing needs in both the rental and ownership sectors. This shortage has led to intense competition among buyers and a surge in home prices.
Impact on Homebuyers
The housing shortage has made homeownership unattainable for many Americans. Home prices have risen more than 30% over the past couple of years, pushing them beyond the reach of millions of potential buyers. During the COVID era, bidding wars became commonplace, with buyers frequently offering well above the listing price in an attempt to secure a home. Today, in an effort to control the inflation rate, the Fed has increased interest rates furthering the unattainability for many Americans. The scarcity of available properties has also given sellers the upper hand, allowing them to dictate terms and potentially waive contingencies.
Again though, with today’s rising costs of goods and interest rates, while still historically low, have made the American Dream of home buying beyond manys reach. Home sellers are now seeing the impacts of lower demand to buy and for the first time in years, home prices are starting to fall leaving many homeowners looking to sell shackled in golden handcuffs and ultimately aiding in the availability crisis.
Impact on Renters
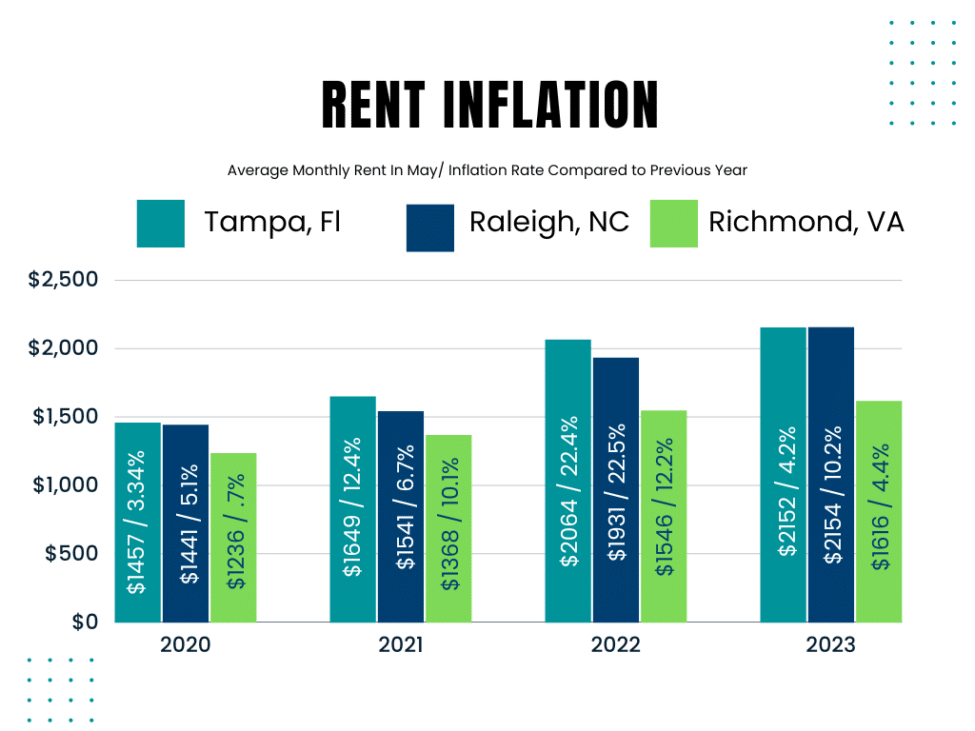
The shortage of available homes has also had a significant impact on renters. As the demand for rental housing increases, rents have been rising sharply. Many individuals and families are struggling to find affordable rental options, leading to financial burdens and limited housing choices. The shortage particularly affects low-income households, exacerbating issues of housing affordability and stability.
Causes of the Housing Shortage
Long-term Underbuilding
One of the primary causes of the housing shortage is long-term underbuilding. Following the housing crash of 2008, many homebuilders went out of business, resulting in a significant decrease in new construction. The housing market has struggled to catch up ever since, with insufficient new homes being built to meet the growing demand.
Coupled with this inability to keep production up, material prices and the need to provide sustainable living wages to employees continue to rise forcing builders to slow production and increase home prices.
Impact of Institutional Investors
The prevalence of institutional investors in the housing market has compounded the shortage. These investors, accounting for more than 13% of all residential real estate purchases in 2021, have acquired a substantial portion of available housing inventory for profit. This acquisition of properties for rental purposes further limits the supply of homes for individual buyers and agitating the rental rates across the nation.
Outdated Zoning Rules
Outdated zoning rules present a significant challenge in addressing the housing shortage. Many cities and towns have zoning regulations that restrict the types of housing that can be built, often allowing only for single-family homes on large lots or high-rise apartment buildings downtown. This lack of “missing middle” housing options, such as townhouses or smaller starter homes, contributes to the shortage of affordable housing.
To combat this, government officials in larger, more densely populated areas like Scarsdale, NY are imposing strict sanctions on urban areas to increase their housing supply by at least 3% every year for the next three years. Not only would this provide more housing but it would include affordable options for those seeking more access to better jobs, schools, and transportation. Currently, the land proposed for affordable multi-family housing units located near the train station is zoned for single-family homes on large lots. In response to this proposed housing, local Amy Paulin declared the “proposal would change the complexity of our county in a way that doesn’t make sense”.
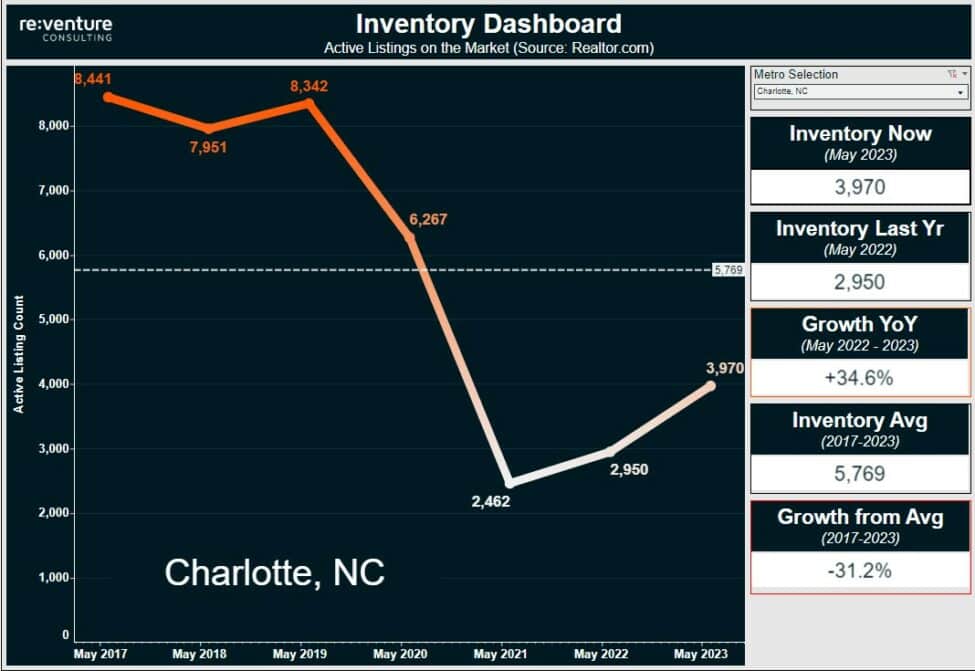
These outdated zoning laws and regulations stretch further around the nation than just densely populated areas like New York. With it’s newfound fame, North Carolina – with its vast untouched landscapes – is also fighting the great fight to keep up with housing demand. Large metros like Charlotte and Raleigh have stretched the capabilities of their infrastructure and are reaching for the skys – if local communities allow. Even stretching beyond city limits into more rural regions, builders are fighting the great fight to secure land with zoning regulations allowing them to build single-family neighborhoods in bulk or multi-family housing units. As with the New York case, many find the disruption to their way of life unmanageable.
Impacts of the Housing Shortage
Affordability Challenges
The housing shortage has resulted in elevated home prices, making homeownership increasingly unaffordable for many Americans. This affordability crisis has forced potential buyers to either delay their plans or settle for homes that may not meet their needs. The shortage also affects renters, as rising demand and limited supply drive up rental prices, placing a significant financial burden on individuals and families.
However, we’re seeing a new type of situation – the accidental landlord. Homeowners shackled with golden handcuffs unable to sell their homes are putting their homes on the rental market. And this may come as a benefit to renters. Those homeowners typically have locked-in lower interest rates. They’re able to increase rental availability and are causing a stir in the rental market by providing cheaper rents than their competition ultimately forcing rents in their area down as a whole. The issue though lies that many of these homeowners will be able to leverage their finances to afford that second home they’ll likely be in for a long time. Increase in rental availability, decrease in rental rates, decrease in available purchasable homes.
Economic Consequences
The housing shortage has far-reaching economic consequences. The increased costs of housing have a direct impact on individuals’ disposable income, limiting their ability to spend on other goods and services. Moreover, the shortage of affordable housing has been estimated to cost the American economy about $2 trillion annually in lower wages and productivity. Slower GDP growth and constrained opportunities for increasing earnings further hinder economic progress.
Housing Market Crash: Debunking Myths and Analyzing the Future
The housing market has always been a topic of great interest and speculation. Homeowners, buyers, and sellers are constantly monitoring its trends, trying to predict the future and make informed decisions. One particular concern that often arises is the possibility of a housing market crash.
Potential Solutions to Address the Housing Shortage
Reforming Zoning Regulations
One key solution to the housing shortage is reforming outdated zoning regulations. Cities and towns need to reconsider their zoning rules to allow for greater housing density and diversity. This may involve relaxing restrictions on accessory dwelling units, promoting mixed-use developments, and encouraging the construction of smaller, more affordable housing options.
Increasing Construction
To bridge the gap between housing demand and supply, there is a need for increased construction efforts. This includes incentivizing homebuilders to construct more affordable housing units and streamlining the construction approval process. Local and state governments can play a crucial role in providing financial incentives, such as tax breaks or grants, to encourage the construction of affordable housing.
Collaboration between Public and Private Sectors
Addressing the housing shortage requires collaboration between the public and private sectors. Public-private partnerships can facilitate the development of affordable housing projects by leveraging resources and expertise from both sectors. Governments can provide land or funding, while private developers can contribute their construction and management capabilities.
A major initiative we’re seeing is the idea of Build To Rent communities. These communities offer a variety of housing options that are specifically built in an effort to boost availability and combat the high housing costs. There are typically only a few variations of homes available in the community allowing builders to spend less on plans and permitting and build homes at a faster pace all without sacrificing the finer details.
Encouraging Innovation in Construction
Embracing innovation in construction techniques and materials can help reduce costs and increase the efficiency of housing production. Modular and prefabricated construction methods, for example, can expedite the building process and potentially lower costs. Additionally, incorporating sustainable design principles can lead to more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly housing options.
Investing in Infrastructure
Investments in infrastructure can contribute to alleviating the housing shortage. Improvements in transportation networks, utilities, and community amenities can make previously inaccessible areas more attractive for housing development. By expanding infrastructure, housing opportunities can be created in regions with greater availability of land and resources.
Conclusion
The housing shortage in the United States is a complex and multifaceted issue with significant impacts on individuals, communities, and the economy as a whole. Addressing this crisis requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses zoning reform, increased construction efforts, collaboration between the public and private sectors, innovation in construction techniques, and investments in infrastructure. By implementing these solutions, it is possible to mitigate the housing shortage and create a more equitable and affordable housing market for all Americans.












